SSSTC in Taiwan makes effective use of rainwater. At SSSTC, 405 m3 of rainwater was recovered in FY2024, equivalent to about 1.2% of the water it used during the same period. The collected rainwater is reused as cooling water for air conditioning equipment, etc.
Effective Use of Water Resources
Approach to Water Resources
In line with Kioxia Group’s Environmental Policy, we continually strive to reduce the environmental impact of the wastewater produced during our manufacturing processes. We recycle the water we use in accordance with our own standards, which are stricter than current legal requirements, in order to conserve precious water resources and ensure business continuity.
Amid worldwide concern over water shortages, Kioxia Group has established the conservation of water resources and ensuring stable operations as business priorities. The balance between supply and demand, the amount of water that can be withdrawn, and the quality of water vary greatly depending on regions. Accordingly, Kioxia Group has identified water-related risks for each region, focusing not only on the short term but on the medium- to long-term as well, and we conduct environmental impact assessments from all angles to ensure appropriate use of water resources. In doing this, we also consider the impact of external environmental factors, such as drought and flooding, on our business operations, as well as the impact of our operations on local water levels.
Water Management Structure
At Kioxia Group, we prioritize all water-related initiatives and indices, seeing these as a key factor in the Group’s sustainability management.
Sustainability strategies and policies, including those related to water, are formulated at Sustainability Strategy Meetings, chaired by the President and CEO, with the degree of target achievement confirmed in each case before a final review by the Board of Directors.
Key performance indicators (KPIs) are discussed and determined by a Sustainability Committee chaired by the executive officer in charge of sustainability, based on sustainability strategies and policies formulated during Sustainability Strategy Meetings, including those related to water.
At Environmental Management Review Meetings, which involve discussions primarily between the officers and division managers responsible for environmental protection, the impact on our business, compliance with relevant laws and regulations, and achievement of our KPIs are all reviewed, with reference to social and legislative trends, and our medium-term environmental plan is evaluated in consideration of the risks and opportunities related to our usage of water.
Issues deliberated at these meetings include the installation of equipment to reduce water consumption during the construction of new plants, and the management of risk through business continuity management (BCM) activities. Assessments of water hazards such as overflowing rivers, large-scale typhoons and drought are also conducted as part of our BCM policy to reinforce our overall management of business risks and enable swift business continuity in the wake of any disaster. Furthermore, specialists investigate and monitor domestic and international regulations and trends to reduce the risks posed to constantly changing water environments.
Evaluating Water Risk
The balance between supply and demand, the amount of water that can be withdrawn, and the quality of water all vary greatly depending on regions. Kioxia Group has commissioned external experts to evaluate water-related risks at our manufacturing site, including Kioxia Corporation’s Yokkaichi Plant, Kioxia Iwate Corporation and Solid State Storage Technology Corporation (SSSTC), from the perspective of current and future supply and demand. These risks are assessed using tools such as the World Resources Institute's (WRI) Aqueduct and the World Wildlife Fund’s (WWF) Water Risk Filter. We use these assessments to analyze risks such as water stress levels and seasonal variations in water supplies through the year 2040 in order to understand the potential impact on our business activities.
An assessment of the Group’s manufacturing sites, confirmed that they are not exposed to any water risk likely to have practical financial or strategic impact prior to the year 2040. This assessment was based on investigations into such factors as water supply and demand risks (driven by seasonal changes, the frequency of droughts, water storage capacity and water source protection levels), the risk of water-related disasters such as flooding or landslides, and regional vulnerability to water pollution that might endanger public health or ecosystems.
Water Resource-related Targets and Results
Using FY2017 levels as the baseline, Kioxia Group has set targets for the reduction of our water intake per unit of storage capacity manufactured, and we manage these using a PDCA cycle.
We set a target for FY2024 of reducing intake to 48.5% or less of FY2017 levels, and achieved this with an actual result of 40.9%.
Going forward, we will continue to pursue activities aimed at achieving water intake reduction targets by both reducing water consumption and by promoting recycling.
Segregated Collection and Recycling of Wastewater Based on Characteristics
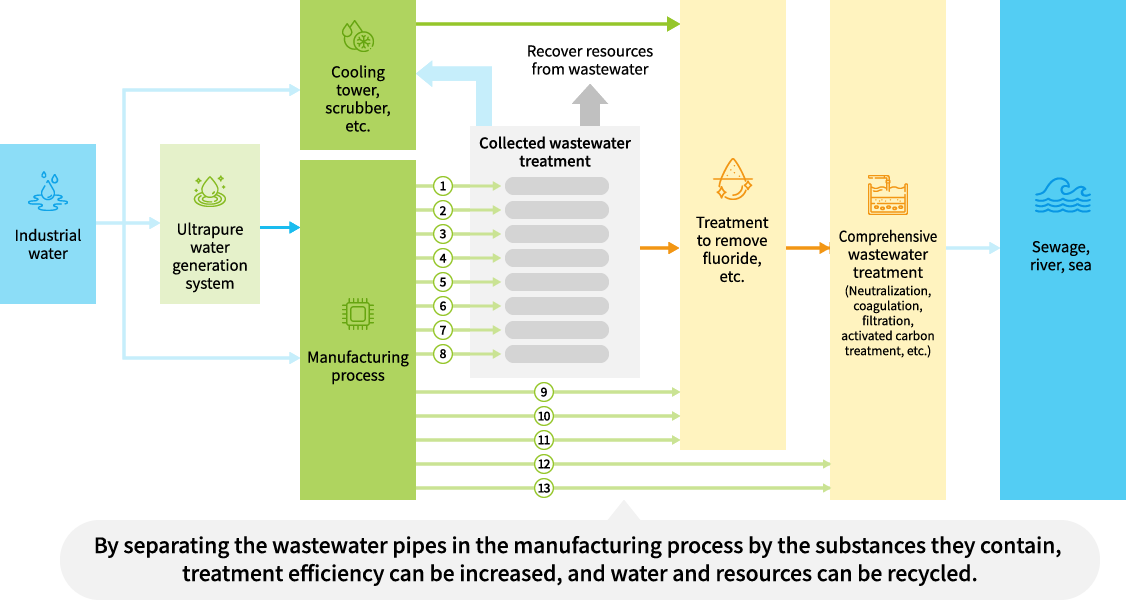
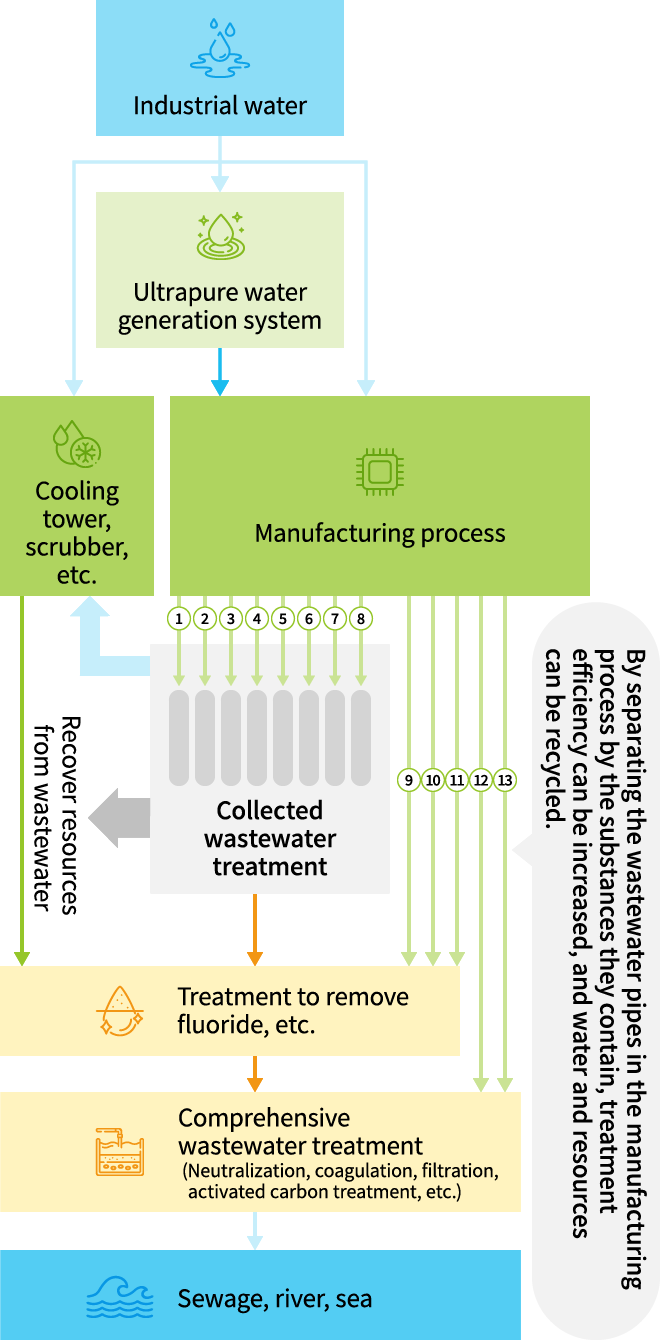
At our manufacturing sites in Japan, our plants are planned and designed around the concept of preserving water and resources. Wastewater pipes leading from manufacturing processes have been configured with up to 13 different lines for different substances contained in the water.
Recyclable wastewater is first treated according to the type of substances it contains during the collection and treatment process, and then reused in facilities such as cooling towers and scrubbers (exhaust gas treatment equipment).
At manufacturing sites in Japan in FY2024, we recycled approximately 37 million m3 of water (approximately 57% of total water usage).
Furthermore, we recover as many resources as possible from wastewater. Some of the materials extracted during the treatment process are sold to external partners where they are recycled into resources.
Since the wastewater pipes are segregated according to the substances contained in the wastewater, we are able to minimize the usage of chemicals and electricity required to recycle and treat the water.
We are also working to reduce water usage in our manufacturing processes. Please see “Reducing Environmental Impact” for details.
Enhanced Wastewater Monitoring
Manufacturing sites of Kioxia Group in Japan treat wastewater appropriately in stages according to its characteristics, and the water quality is checked before it is discharged off site. Our manufacturing plants monitor wastewater using voluntary standards that are more stringent than the prevailing legal requirements in order to minimize the impact of our business operations on the atmosphere and on rivers.
Around-the-clock, automated monitoring is conducted in respect of legally regulated factors, including chemical oxygen demand (COD), suspended solids (SS), fluorine (F), and hydrogen ion (pH) levels. Kioxia Group in Japan also voluntarily controls items not subject to legal restrictions through sampling conducted at Analysis Centers located within our manufacturing plants. These centers conduct around 47,800 water-related tests in FY2024.
As during the previous fiscal year, Kioxia Group was not subject to any government fines or penalties related to wastewater in FY2024.
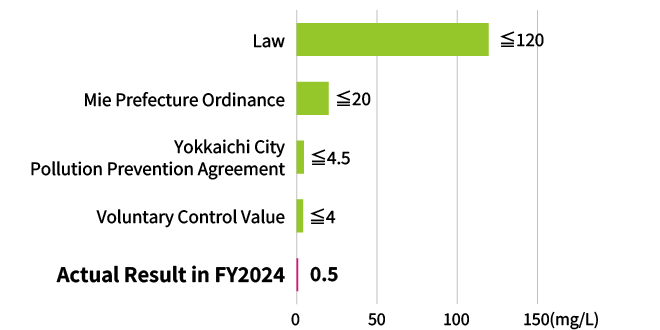
Wastewater BOD (Biochemical Oxygen Demand) Concentration Control Values for River Discharge
(Kioxia Corporation’s Yokkaichi Plant)
Effective Use of Rainwater
Aiming for Appropriate Water Use
At Kioxia Group’s manufacturing sites in Japan, procedures are in place to recover and recirculate unused ultra-pure water used for wafer cleaning. Additionally, the flow rate is adjusted in stages according to changes in water usage within the manufacturing process, maintaining consistent water quality and appropriate water volume.