Led mainly by the taskforce on the environment, we are currently identifying the risks and opportunities related to our businesses and verifying their potential impacts on climate change, including calculation of financial impact. Risks deemed to be of high importance are discussed at the Sustainability Strategy Meeting and the Sustainability Committee to consider a response. In addition, the Group maps and analyzes sustainability issues and risks affecting its business models, value chain, and relevant stakeholders, and works to avoid and mitigate the risks.
Climate Change
Initiatives to address climate change are a management priority for Kioxia Group as we seek to help achieve a decarbonized society. We refer to these priority areas as “sustainability materiality.” We aim to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and energy consumption across our operations—both in terms of our business activities and product lifecycles—throughout our value chain.
Aiming to Achieve Net-zero Greenhouse Gas Emissions by 2050
With the aim of contributing to the reduction of greenhouse gas emissions agreed under the Paris Agreement, in April 2023 Kioxia Group announced that by FY2050 we aim to achieve net-zero Scope 1 emissions (direct emissions from our business sites) and Scope 2 emissions (indirect emissions from our use of purchased energy) across our global operations by offsetting the amount of emitted greenhouse gas against the amount of emissions absorbed or eliminated.
We have additionally set a target of procuring 100% of our energy from renewable sources by FY2040. In January 2023, we began introducing on-site solar power generation systems, with the third such system commencing operation in July 2024. We will continue to promote the use of renewable energy going forward.
Regarding direct emissions from our manufacturing sites, since 2011 we have installed abatement equipment in 100% of our targeted facilities, aiming to eliminate during our manufacturing processes the emission of PFCs1 with high global warming potential.
In 2024, we completed construction of Kitakami Plant Fab2 (“K2”) at Kioxia Iwate Corporation, incorporating the accumulated environmental technologies of Kioxia Group to contribute to energy conservation.
Based on an energy management system that was commissioned at our domestic manufacturing sites in 2024, we will continue implementing measures to address climate change in the course of our business activities in coordination with our existing energy conservation initiatives.
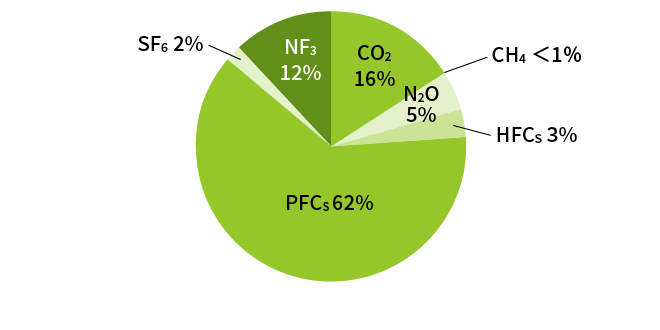
- 1 CFC alternatives with high global warming potential used in semiconductor manufacturing. Those used by Kioxia Group include CF₄, C₄F₈, CHF₃, SF₆, NF₃, CH₂F₂, CH₃F, CH₄, and N₂O

Disclosures Aligned to TCFD Recommendations
In June 2021, Kioxia Group announced our endorsement of the recommendations published by the Task Force on Climate-Related Financial Disclosures (TCFD).2 We believe that accurately ascertaining the climate-related impact of our business, disclosing such information to stakeholders, and deepening mutual understanding are indispensable for achieving sustainable corporate growth, and we proactively disclose that information in accordance with the TCFD recommendations.
- 2 A task force established by the Financial Stability Board that devises methods of disclosing climate-related financial information to promote the disclosure of information related to climate-related risks and opportunities
Governance
Kioxia Group undertakes various activities aimed at mitigating climate change under its sustainability management structure.
At the Sustainability Strategy Meeting chaired by the President and CEO, executive officers discuss our strategies and policies and check the level of achievement, while consulting with the Board of Directors on key issues. The Sustainability Committee, chaired by the Executive Officer in Charge of Sustainability, discusses and formulates key themes, including climate change, and sets key performance indicators (KPIs) based on the strategies and policies formulated at the Sustainability Strategy Meeting.
We have also set up various subordinate taskforces to tackle important sustainability issues across the organization. These taskforces report on their areas of focus and progress to the Sustainability Committee. We are reviewing the impact of climate change by referencing the following items, based on the TCFD recommendations: scenario analysis, analysis of climate-related risks and opportunities, and strategies, metrics and targets.
For more information on how we promote sustainability, please refer to "Sustainability Management" below.
Risk Management
Strategy
Scenario Analysis
Kioxia Group analyzes the impact of climate change on our operations, considering its effects on stakeholders, business activities, and overall value chain. We conduct assessments using the 1.5 °C , 2 °C , and 4 °C Scenarios stipulated by the International Energy Agency (IEA) and other organizations.3
Under the 1.5 °C Scenario, we believe government action, regulatory strengthening and the preferences of customers and other stakeholders will have a significant impact. For example, we assume that there will be an increase in the costs associated with the implementation of measures to reduce greenhouse gas emissions at manufacturing sites, and higher research and development costs arising from the need to develop more energy-efficient products with increased capacity. In addition, we envisage expansion of decarbonization-related technologies and markets, as well as the spread of renewable energy, and the achievement of decarbonization and efficiency gains.
Under the 4 °C Scenario, we project the emergence of physical risks to our company bases.
- 3 These are terms commonly applied to climate-related scenarios depicted by the IEA and other organizations. Each scenario includes specifications of the economic measures needed to suppress rising temperatures and the envisaged environmental damage in the event such increases in temperature occur.
Risks and Opportunities
Kioxia Group assesses risks and opportunities in both the short and medium-to-long term, based on scenario analysis. The potential risks and opportunities envisaged as of 2030 are outlined in the table below.
We recognize the transition risks posed by the migration to a low-carbon economy, such as increased power supply costs resulting from the introduction of a carbon tax, and the cost of installing additional equipment to remove PFCs in line with increases in our manufacturing output. In addition, we recognize the potential for physical risks such as an increase in cleanroom air-conditioning costs resulting from a rise in outdoor temperatures.
In terms of potential opportunities arising from the transition to low-carbon economies, we envisage expanding business opportunities through the manufacture of more efficient products that consume less electricity, the reduction of our own power consumption during manufacturing through the implementation of energy conservation measures, and the increase in revenue from sale of surplus emissions reduction credits.
To clarify the potential effects of climate-related risks and opportunities on our business activities, our Environment Task Force, working under the Sustainability Committee, conducts detailed calculations of their financial impact. Given the expansion of our business and the demand from our stakeholders for us to respond to climate change, we believe that the financial impact of both risks and opportunities in our research and development, our transactions with customers, and the cost of our electricity will be significant, regardless of the scenario. However, we believe that the cost of installing PFCs abatement equipment and the associated renewable energy and energy-saving equipment will have a relatively small financial impact.
We will continue to address any risks related to climate change, seeing these more as opportunities.
* Table can be scrolled horizontally.
| External Events | Risks | Opportunities | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Type | Potential Financial Impact | Type | Potential Financial Impact | |||
| Introduction of carbon pricing (e.g., incorporating carbon taxes) | (Transition Risks) Policy and Legal |
|
(Transition Opportunities) Energy Sources |
|
||
| Conversion to renewable energy | (Transition Risks) Technology |
|
(Transition Opportunities) Energy Sources |
|
||
| (Transition Opportunities) Resource Efficiency |
|
|||||
| Stricter promotion of energy-saving measures during manufacturing | (Transition Risks) Technology |
|
||||
| Improving environmental awareness of stakeholders | (Transition Risks) Markets |
|
(Transition Opportunities) Products |
|
||
| (Transition Risks) Reputation |
|
(Transition Opportunities) Markets |
|
|||
| Transition to manufacture of low-carbon products | (Transition Risks) Reputation |
|
(Transition Opportunities) Markets |
|
||
| (Transition Risks) Technology |
|
|||||
| Upgrading power infrastructure | (Transition Risks) Technology |
|
(Transition Opportunities) Energy Sources |
|
||
Extreme weather conditions |
(Physical Risks) Acute |
|
― | ― | ||
| Water shortages | (Physical Risks) Chronic |
|
― | ― | ||
| Rising temperatures | (Physical Risks) Chronic |
|
― | ― | ||

- Introduction of renewable energy
- Promotion of energy-saving activities
- Efficient use of water resources
- Development of high-capacity products with highly efficient energy consumption
- Reinforcing BCM and supplier engagement
- Introduction of carbon credits
- Preserving natural capital and promoting biodiversity
4 Business Continuity Management
Metrics and Targets
To help achieve our goal of net-zero greenhouse gas emissions by FY2050, Kioxia Group has established KPIs related to our energy consumption, our environmental impact, and the use of our products. We review the degree of achievement of these at Environmental Management Review meetings held every six months.
For example, with regard to Scope 2-related energy consumption, we are promoting energy-saving activities with the stated goal of reducing the volume of emissions by 1% each year compared with the previous fiscal year. For details, please refer to “Greenhouse Gas Emissions across our Entire Value Chain” and “Efforts to Adapt to Climate Change” below.
Moreover, we have set the long-term goal of using 100% renewable energy by FY2040. Through the creation of an energy portfolio that incorporates energy conservation activities, we will work to secure the optimal and stable procurement of renewable energy in line with the expansion of our business. We will also work to install renewable power generation systems and carbon-neutral city gas supplies in our plants.
Greenhouse Gas Emissions across Our Entire Value Chain
Scope 1, 2 and 3 CO2-equivalent greenhouse gas emissions from Kioxia Group’s business operations in FY2024 are shown in the chart below. The figures in the table below cover emissions from Kioxia Corporation, including the company’s Head Office, Yokohama Technology Campus and Yokkaichi Plant, Kioxia Iwate Corporation, and Solid State Storage Technology Corporation (SSSTC).
(Dash cells (―) in the below table indicate “not applicable”)
Scope 1 (Direct emissions)
|
CO2 Emissions in FY2024 (t-CO2) |
Category Outlines |
|---|---|
|
510,800 |
Direct emissions from in-house fuel use and our business processes |
Scope 2 (Indirect emissions)
|
CO2 Emissions in FY2024 (t-CO2) |
Category Outlines |
|---|---|
|
1,951,000 |
Indirect emissions from the production of electricity, heat and steam purchased by the company |
Scope 3 (Other indirect emissions not covered under Scope 1 and 2)
* Table can be scrolled horizontally.
|
Category |
CO2 Emissions in FY2024 |
Category Outlines |
|---|---|---|
|
1. Purchased goods and services |
5,489,294 |
Emissions resulting from activities up to the processing of raw materials and the manufacture of parts, packaging, etc. |
|
2. Capital goods |
634,589 |
Emissions resulting from the construction and manufacture of our own capital goods |
|
3. Fuel- and energy-related activities not included under Scope 1 or 2 |
364,496 |
Upstream emissions of purchased fuels/electricity, etc. |
|
4. Upstream transportation and distribution |
7,023 |
Emissions arising from the transportation of products and waste in Japan (excluding overseas transportation and suppliers’ transportation) |
|
5. Waste generated in operations |
22,267 |
Emissions from the treatment of waste |
|
6. Business travel |
1,407 |
Emissions arising from employees’ business travel |
|
7. Employee commuting |
12,202 |
Emissions arising from employees’ commuting |
|
8. Upstream leased assets |
― |
― |
|
9. Downstream transportation and distribution |
― |
― |
|
10. Processing of sold products |
― |
― |
|
11. Use of sold products |
605,155 |
Emissions arising from the use of sold products |
|
12. End-of-life treatment of sold products |
― |
― |
|
13. Downstream leased assets |
― |
― |
|
14. Franchises |
― |
― |
|
15. Investments |
― |
― |
|
Scope 3 (Total) |
7,136,433 |
Breakdown of Scope 1 Direct Emissions (FY2024)
Achievements in the Areas of Energy Consumption and Greenhouse Gas Emissions
The graph below shows Kioxia Group’s energy consumption and Scope 1 and 2 greenhouse gas emissions. In order to achieve our goal of 100% renewable energy usage by FY2040 and net-zero greenhouse gas emissions by FY2050, we are introducing renewable energy and other initiatives.
Since June 2024, Kioxia Corporation have been participating in the Catalyze Program5 as a supplier, helping the industry’s transition to renewable energy.
- 5 A collaboration between sponsoring companies and Schneider Electric SE, with the aim of accelerating the transition to the use of renewable energy by involving suppliers in the semiconductor industry. Suppliers providing products to sponsor companies can take advantage of benefits such as insights and information useful for the introduction of renewable energy by participating in this program.
As of June 2025, the companies sponsoring the program include Applied Materials, ASM, Cisco, Edwards, Google, HP, Intel and Lam Research.
https://hub.zeigo.com/catalyze
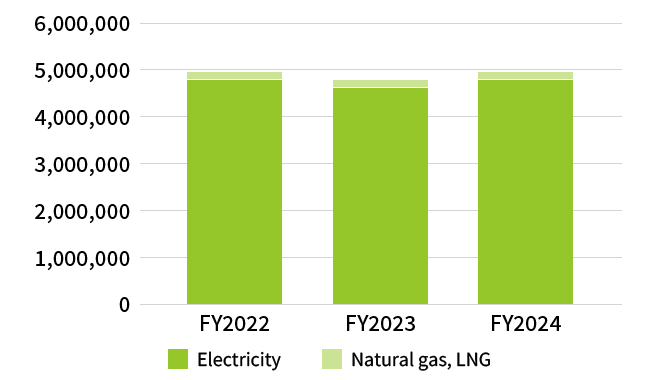
Amount of Energy Used (MWh)
Notes:
1 The percentage of our total energy consumption accounted for by renewable energy in FY2024 was 4.7%.
2 Data covers Kioxia Corporation, Kioxia Iwate Corporation and SSSTC.
Scope 1 + Scope 2 Emissions (t-CO2)
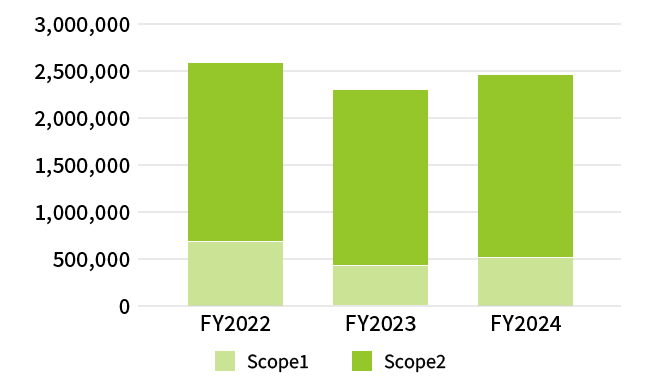
Note: Data covers Kioxia Corporation, Kioxia Iwate Corporation and SSSTC.
Efforts to Adapt to Climate Change
Kioxia Group is advancing efforts to adapt to climate change throughout our value chain, taking into account the identified risks, opportunities and their impact.
Product Development
In the data storage market, the need for low-power consumption-type products is growing extremely rapidly, and we expect to expand sales opportunities by further developing these products. We are working on the research and development of more energy-efficient processes and increased capacity through the development of advanced integration technology. Specifically, we have set the challenging target of reducing the energy consumption of our memory and SSD products by 50% per unit of 1 GB data from FY2017 levels by FY2025.
To gauge the environmental impact of our products during manufacture and use, Kioxia Group has started applying the Life Cycle Assessment (LCA) method6 for certain products. In FY2024, we conducted third-party verification for four products.
- 6 A method for quantitatively assessing the environmental impact of a product or service throughout its lifecycle (raw material extraction, manufacture, transportation, usage, and waste disposal or recycling) or at a specific stage in its lifecycle.
Please refer to “Reducing Environmental Impact through Our Products” for details.
Operation of Manufacturing Sites and Research Development Facilities
Kioxia Group has set the goal of achieving net-zero Scope 1 direct emissions and Scope 2 indirect emissions resulting from our use of purchased energy by FY2050.
To help achieve the reduction of Scope 1 emissions, we have been proactive in the installation of abatement equipment to deal with PFCs—greenhouse gases with high global warming potential. Since 2011, we have installed PFCs abatement equipment in 100% of the target facilities. We are striving to improve the efficiency of operations through the introduction of online monitoring via the Internet of Things (IoT) and to enhance the performance of abatement equipment in cooperation with our suppliers. The reduction effect of this abatement equipment on PFCs in FY2024 was 4.66 million t-CO2.7
We have also started using carbon-neutral city gas.
Contribution of PFCs Abatement Equipment to Scope 1 Direct Emissions Reduction (t-CO₂)
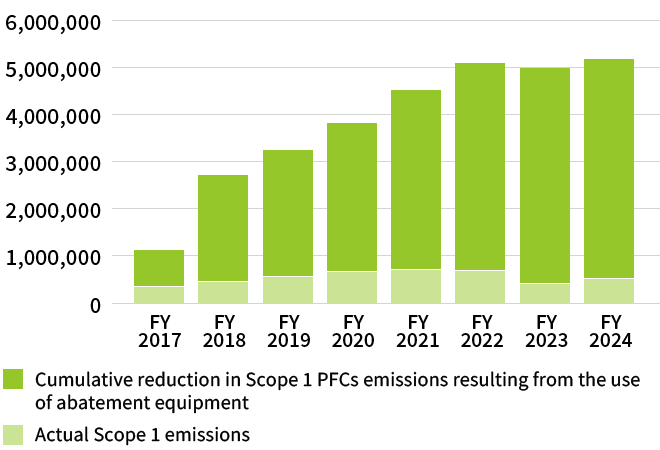
Note: Covers Kioxia Corporation, Kioxia Iwate Corporation and SSSTC (SSSTC results are for the period from FY2021 onward).
7 Calculated based on IPCC guidelines
Use of Gas with Low Global Warming Potential
We are working to optimize the types of gas used in the fabrication of memory circuits, and the processing conditions under which such gases are used.
BiCS FLASH™ generation 8 is a product that requires high processing precision. By switching to a gas with a lower global warming potential,1 we have increased processing efficiency per volume of energy input by approximately 25%2 in terms of volume produced per energy input, which is helping to conserve energy.
- 1 Use of gas with a global warming potential of less than 1.
- 2 For certain processes, compared with the previous gas that was used.
Please refer to this article for details.
As the latest fab of Kioxia Group, Kioxia Iwate Corporation’s K2 fab has been designed with climate change mitigation and adaptation in mind.
The air conditioning inside the cleanroom is important for ensuring product quality, and factors such as the air conditioning method, cooling and heat source system, and waste heat recovery system have been comprehensively redesigned compared with previous systems. These highly efficient systems are expected to be able to reduce the amount of power used for ventilation and for heating and cooling by 30% or more.
In addition, the wastewater treatment facility is designed to take advantage of the site’s natural elevation. Conventionally, wastewater is pumped via a relay tank located in the basement of the facility to an outdoor treatment facility. In the K2 fab, however, water flows directly from the manufacturing process to the treatment facility by gravity. This has not only eliminated the use of electricity for pumping, but has also helped to reduce the building’s carbon footprint by eliminating the concrete and pump equipment that would be needed for constructing a relay tank.
We will continue to reduce the amount of Scope 2 indirect emissions resulting from our use of purchased energy by conserving energy and making greater use of renewable energy sources. Kioxia Group’s manufacturing sites have energy management systems built to comply with ISO 50001. In order to optimize the efficiency of our energy consumption, we have the stated goal of reducing Scope 2 energy consumption by 1% each year compared with the previous fiscal year, in line with the directives contained in the Act on Rationalizing Energy Use and Shifting to Non-fossil Energy (hereinafter, “the Energy-Saving Act”) in Japan.
In FY2024, we achieved our goal for emissions reduction through various energy-saving activities, recording an actual reduction of 24,000 t-CO2 per year against a target of at least 20,000 t-CO2 per year. From FY2017 through FY2024, our energy conservation efforts have resulted in a cumulative reduction of approximately 170,000 t-CO2.
To promote energy conservation and efficiency at each facility, we endeavor to improve and incorporate new technologies. These include technologies for smart factories and waste heat utilization, as well as improvements in manufacturing and testing processes and temperature management of auxiliary equipment. We have established processes whereby we periodically address priority areas and assess the progress of improvements.
Monitoring of CO2 Emissions
Kioxia Group has also started internally monitoring CO2 emissions to improve the operational efficiency of our manufacturing facilities and raise awareness of the need for energy conservation. At SSSTC, we have introduced a system that tracks and monitors the sources and amounts of CO2 emissions at each business site. We are also creating an environment that raises employees’ awareness of energy conservation and efficiency at domestic manufacturing sites, for example, by posting the CO2 emissions of our plants on the company intranet.
Promoting Energy Conservation
At Kioxia Corporation’s Yokkaichi Plant and Kioxia Iwate Corporation, our energy-saving promotion team is leading efforts to improve the energy efficiency of business operations. We have also set up subcommittees for each target facility and manufacturing process, who select key items and check the progress of these in collaboration with other departments. Since 2019, the combined number of items and projects monitored at both plants has exceeded 1,900, resulting in a cumulative CO2 emissions reduction of more than 140,000 t-CO2.
Since 2020, Kioxia Corporation’s Yokkaichi Plant has been working with the Mie University Graduate School of Engineering and Graduate School of Regional Innovation Studies on a joint industry-academia project, “Electric Power Strategy in a Semiconductor Mega Fab.” One result of the project has been the development of a freezer operation regulation tool. Previously, freezer operation relied on the experience of the operator, but the tool now provides on-screen guidance to facilitate optimal operation based on conditions such as operating load and outside temperature and humidity. In FY2024, the tool reduced CO2 emissions by approximately 2,500 t-CO2, and we plan to roll it out across more facilities going forward.
Kioxia Iwate Corporation is preparing the cleanroom environment for its K2 fab ahead of full-scale operation. By optimizing ventilation capacity to maintain air pressure within a range that does not affect product quality, we achieved a reduction of 475 t-CO2 in FY2024.
Structured energy-saving activities have been carried out at SSSTC, with nine key initiatives in FY2024 resulting in a reduction of 95 t-CO2.
Value Chains
As climate change continues in the form of global warming, damage caused by water-related natural disasters including typhoons and heavy rains is becoming more apparent every year. These events have an impact on the production of suppliers and logistics, increasing the risk of disruption to our manufacturing processes and product supplies.
Kioxia Group includes all business units within the scope of its business continuity management (BCM) policy, and has established response protocols that address a variety of risks, including natural disasters. Under our BCM policy, we monitor the status of our materials and products during normal operations, and ensure we have multiple suppliers. Furthermore, we are making efforts to ensure we are able to swiftly assess the situation in the event of an emergency, and to minimize any effects on the business at such times by means of a collaborative process designed to ensure the early recovery of services.
Addressing climate change is also an important issue for our customers and suppliers. Kioxia Group collects environmental impact data from its key suppliers through the CDP Supply Chain Program, and analyzes this information to support the reduction of its Scope 3 emissions. For suppliers who have a major impact on Kioxia Group’s Scope 3 emissions, we engage in individual discussions to share challenges and explore solutions. In FY2024, we conducted individual consultations on environmental impact reduction with multiple suppliers accounting for around one-third of our total procurement value.
We will continue to work with our partners across the entire value chain and help realize a decarbonized society.
Decarbonization of the PCB (Printed Circuit Board) Assembly Process in Cooperation with a Customer
Kioxia Corporation developed a PCB assembly process with Lenovo Corporation by using a low-temperature solder technology developed by Lenovo Corporation. Compared with the solder previously used, this new solder enables a lower maximum heating temperature in the reflow furnace, resulting in reduction of electricity consumption and carbon emissions in the PCB assembly process.*
This solder is used by external partners who undertake SSD assembly for certain SSD products.
- Compared with Pb-free (Sn-Ag-Cu) solder
Taking Part in External Initiatives Related to Climate Change
Kioxia Group is helping to address climate change, gathering information and making recommendations to the government through participation in industry associations and other activities.
Following the announcement by Kioxia Holdings Corporation of its endorsement of the TCFD recommendations in 2021, we have been participating in the activities of the TCFD Consortium since 2022. In 2024, we also joined the Semiconductor Climate Consortium (SCC), established by the industry association Semiconductor Equipment and Materials International (SEMI). As a member of the semiconductor value chain, we are accelerating efforts to address climate change.
Kioxia Corporation is helping to address energy and global warming issues as a member of the Environmental Working Group of the Japan Electronics and Information Technology Industries Association (JEITA), a group representing the electronic device industry. As a supporting member of the Japan Climate Leaders’ Partnership (JCLP), a corporate alliance that aims to achieve a decarbonized society, we collaborate in measures aimed at achieving the 1.5 °C target stipulated in the Paris Agreement, as well as in discussions about proposals to be made to the government.