Social Trends
Contributing to Convenient and Comfortable Lifestyles
Making data more widely available will help achieve improved lifestyles for even more people.
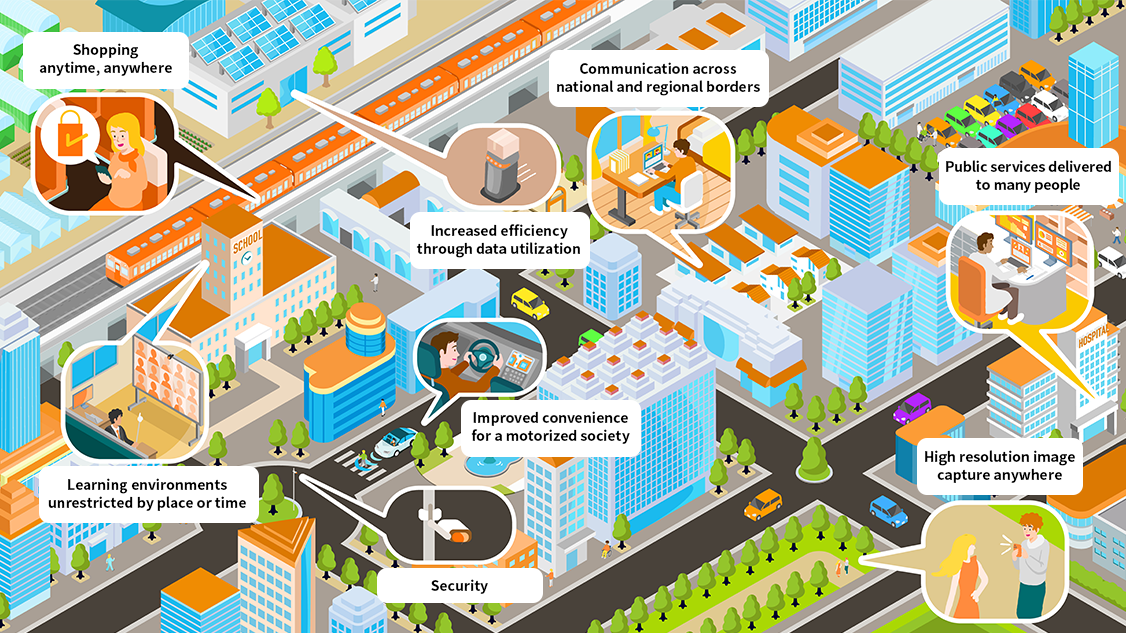
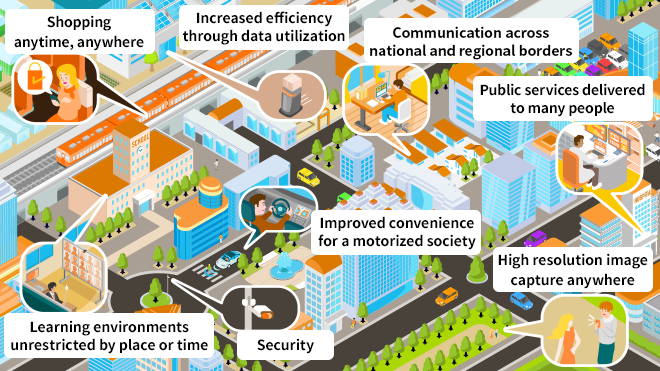
By enhancing high-capacity, high-speed, low-power-consumption,
and high-reliability technologies, and making people’s lifestyles smarter,
we will help create a society
in which more people can lead convenient and comfortable lives.
By enhancing high-capacity, high-speed, low-power-consumption, and high-reliability technologies, and making people’s lifestyles smarter, we will help create a society in which more people can lead convenient and comfortable lives.
Note: The information on this page is current as of the date of the announcement.
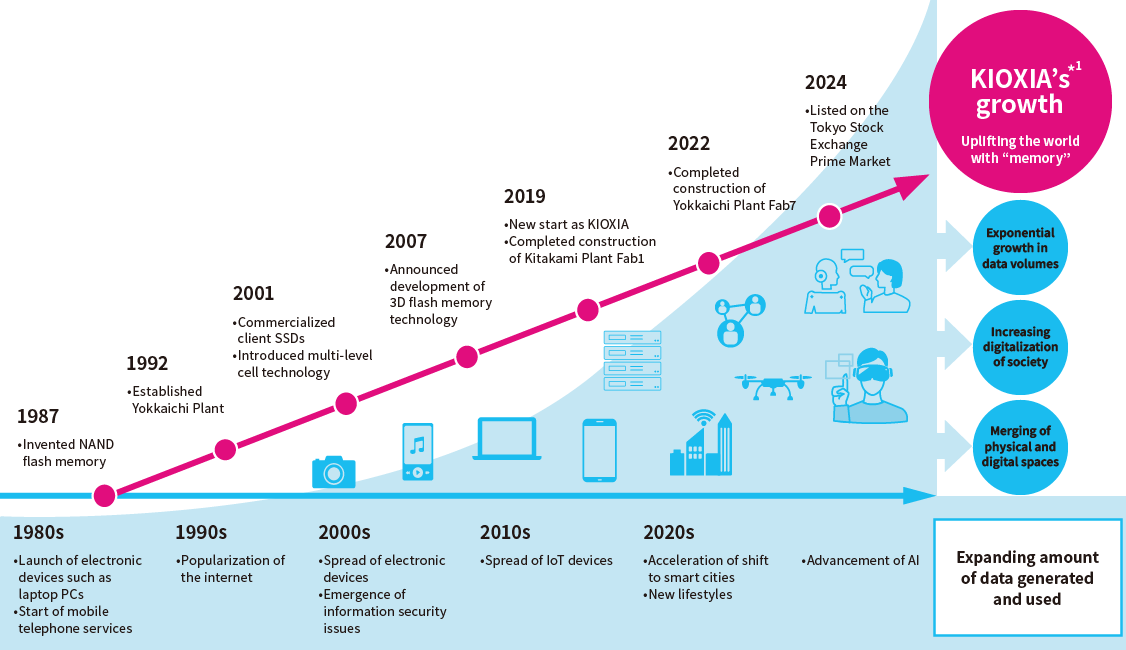
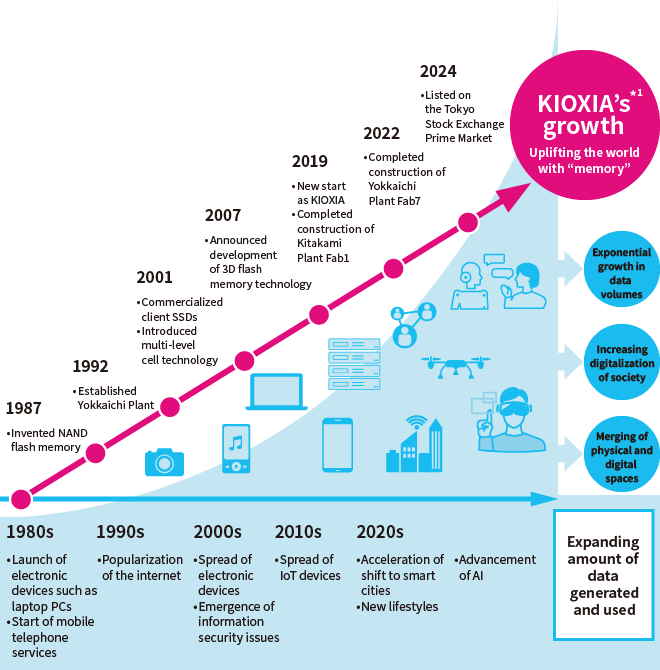
Kioxia Group is responding in a sustainable manner to the evolution of a digital society and the increasing demand for data
KIOXIA’s semiconductor memory technologies, typified by the NAND flash memory it invented in 1987, have supported the emergence of digital devices and the evolution of a digital society. As the amount of data generated increases exponentially with the use of AI, IoT and big data, new needs and issues are expected to arise. Always in touch with the times, we will continue to innovate and provide society with new products and services.
Kioxia Group will continue to evolve with society, based on its mission of “uplifting the world with ‘memory.’”
- *1 In 2017, the memory business of Toshiba Corporation was incorporated into a separate company, which commenced operations as Toshiba Memory Corporation. The company changed its name to Kioxia Corporation in 2019.
1980s
From the 1970s, semiconductor manufacturing boomed in Japan, and it became an essential element of the country’s industrial sector.
In the 1980s came the first steps in the evolution of a digital society with the launch of new electronic devices such as laptop PCs and video game consoles, and the start of mobile telephone services in Japan.

KIOXIA
1987: Invented NAND Flash Memory
KIOXIA invented NAND flash memory in 1987. Flash memory is an extremely small semiconductor storage device. Prior to the launch of NAND flash memory, magnetic tape and disks that required no power source were the mainstream storage devices. NAND flash memory offered the distinct advantages of short read/write speed and the potential for miniaturization.
1990s
Social Trends
By the early 1990s, PCs had become ubiquitous and the internet started to become popular with the advent of the World Wide Web. The dial-up connections used to connect to the internet at the time were a far cry from the high-speed connections commonly used today.
Digital cameras then appeared. Playing a part in this technological innovation were memory cards that store image data.

KIOXIA
1991: Commercialized the world's first 4 Mbit NAND flash memory (the world's first NAND flash memory commercialization)*
1992: Established Yokkaichi Plant
Yokkaichi Plant was established for the mass production of memory products that were state of the art at the time. Production of NAND flash memory started at Yokkaichi Plant in 1999.

Yokkaichi Plant at the time of its establishment (1992)
2000s
Social Trends
Digital devices such as mobile phones, portable music players and digital cameras became prevalent in the early ‘2000s, and advances were made in compression technology for audio and video data. In response, demand grew for flash memory as a high-capacity, high-performance recording medium.
Mobile phones with integrated digital cameras emerged, and the start of third-generation (3G) telecommunication services enabled high-speed, high-capacity data transmission, paving the way for the use of email and internet access on mobile phones.

KIOXIA
2001: Commercialized 1 Gbit MLC (160 nm generation) NAND flash memory, which was the world’s first application of multi-level cell technology to a NAND flash memory product*
2007: Announced Development of 3D Flash Memory Technology
At the time, the miniaturization technology used to increase flash memory capacity (the number of memory cells per plane) was reaching its physical limits.
In response, in 2007 KIOXIA announced the development of the world’s first 3D flash memory technology in which multiple memory cells were stacked. To reduce manufacturing costs, an innovative technology known as BiCS FLASH™ was used whereby plate-shaped electrodes were stacked and through which vertical holes were punched for electrodes, thereby creating memory cells in all the layers at once.

2007: Announced industry’s largest capacity 128GB SATA SSD*
Solid state drives (SSDs) began to replace hard disk drives (HDDs) in laptop PCs, leading to significantly higher performance, reduced weight and lower prices.
2010s
Social Trends
The use of flash memory in smartphones became commonplace, enabling portable devices to store large images and music.
A range of electronic devices appeared, including wearable devices, smart speakers and VR headsets, and the volume of data traffic increased exponentially with the increasing popularity of the internet and cloud computing. Digital technology had become an essential part of daily life.

KIOXIA
2016: Started mass production of 3D flash memory BiCS FLASH™
2017: Established Toshiba Memory Corporation (currently Kioxia Corporation)
2019: Established Toshiba Memory Holdings Corporation (subsequently Kioxia Holdings Corporation) on March 1
2019: Made a fresh start as Kioxia Group
On October 1, 2019, Toshiba Memory Holdings Corporation changed its company name to Kioxia Holdings Corporation in order to mark a fresh start.

2020 Onward
Social Trends
The development of digital technology has changed people’s lifestyles in a number of ways. These include more efficient economic activity through the use of data, and the ability to communicate via the internet across national and regional boundaries.
A growing array of new needs and issues is expected, ranging from ongoing growth in the amount of data people generate through the use of AI, IoT and big data in the fields of autonomous driving and telemedicine.

KIOXIA
July 2020: Completed acquisition of Solid State Storage Technology Corporation, a subsidiary of Taiwan-based LITE-ON Technology Corporation
October 2022: Completed Fab7 at Yokkaichi Plant
Fab7 has the capability to produce sixth-generation, 162-layer flash memory and future advanced 3D flash memory.
June 2023: Commenced operation of two new R&D facilities
The operation of new R&D facilities in Yokohama is strengthening our R&D capabilities and promoting further advancement in technological innovation.
December 2024: Listed on the Tokyo Stock Exchange Prime Market
Kioxia Group will continue using its memory technologies to provide new value,
allowing people to lead more convenient and comfortable lives in a digital society.